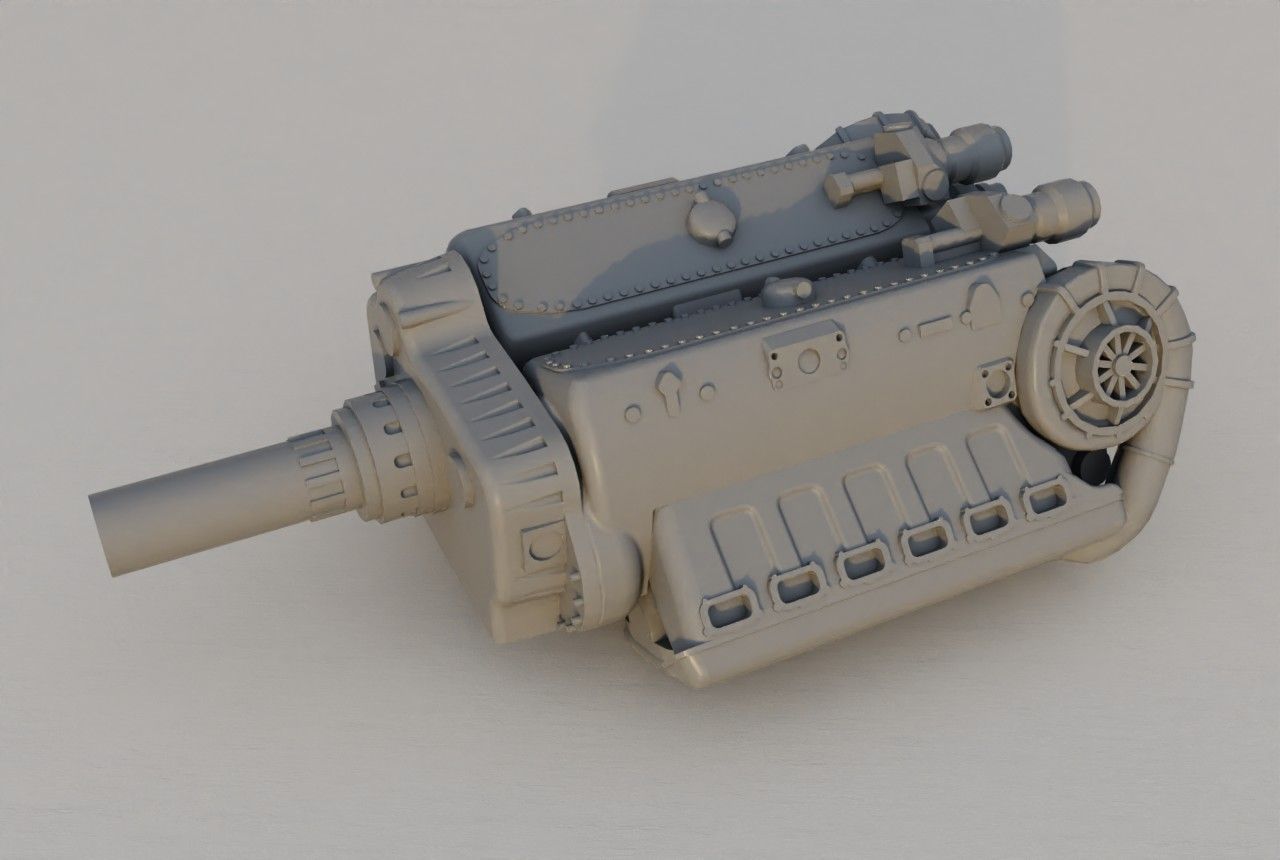
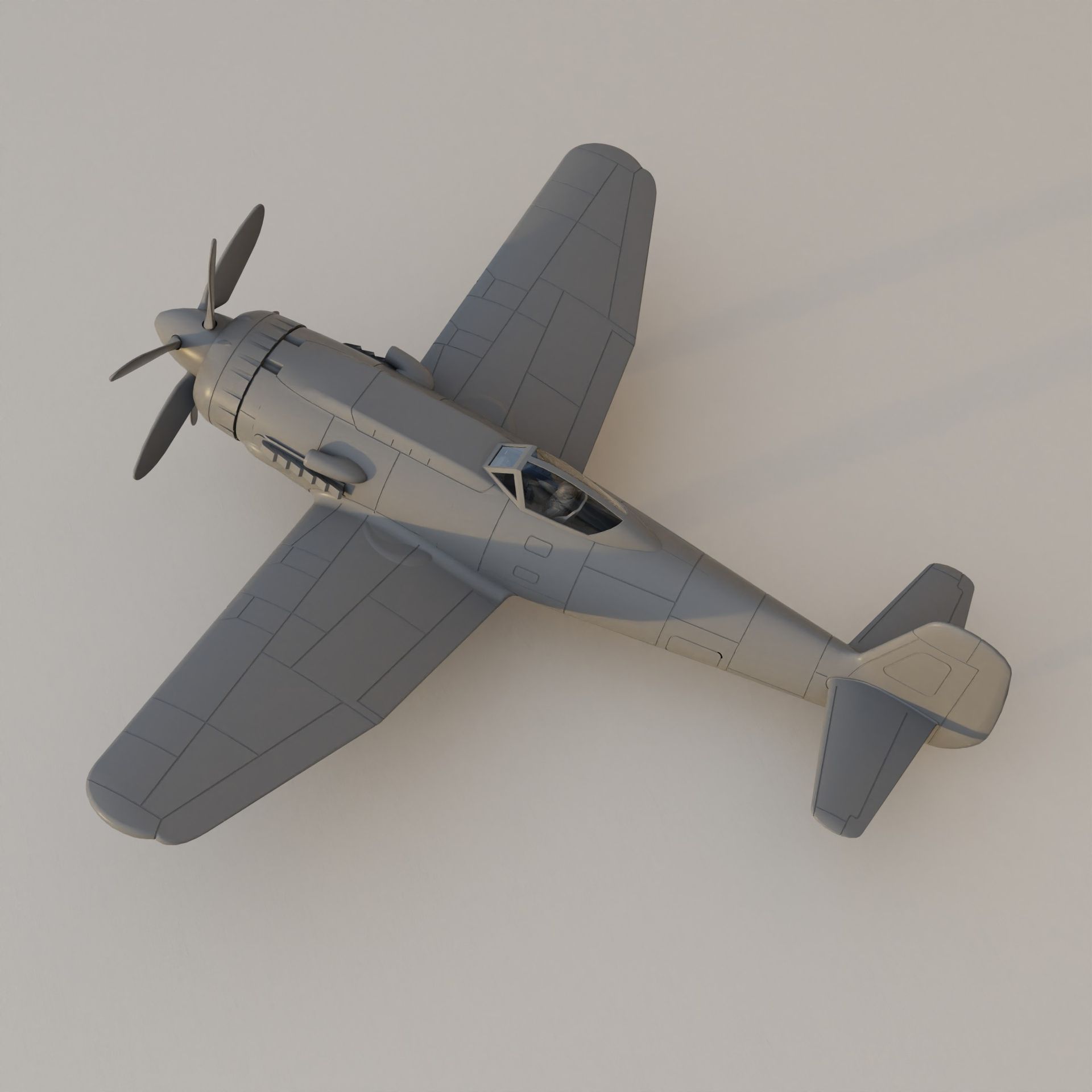
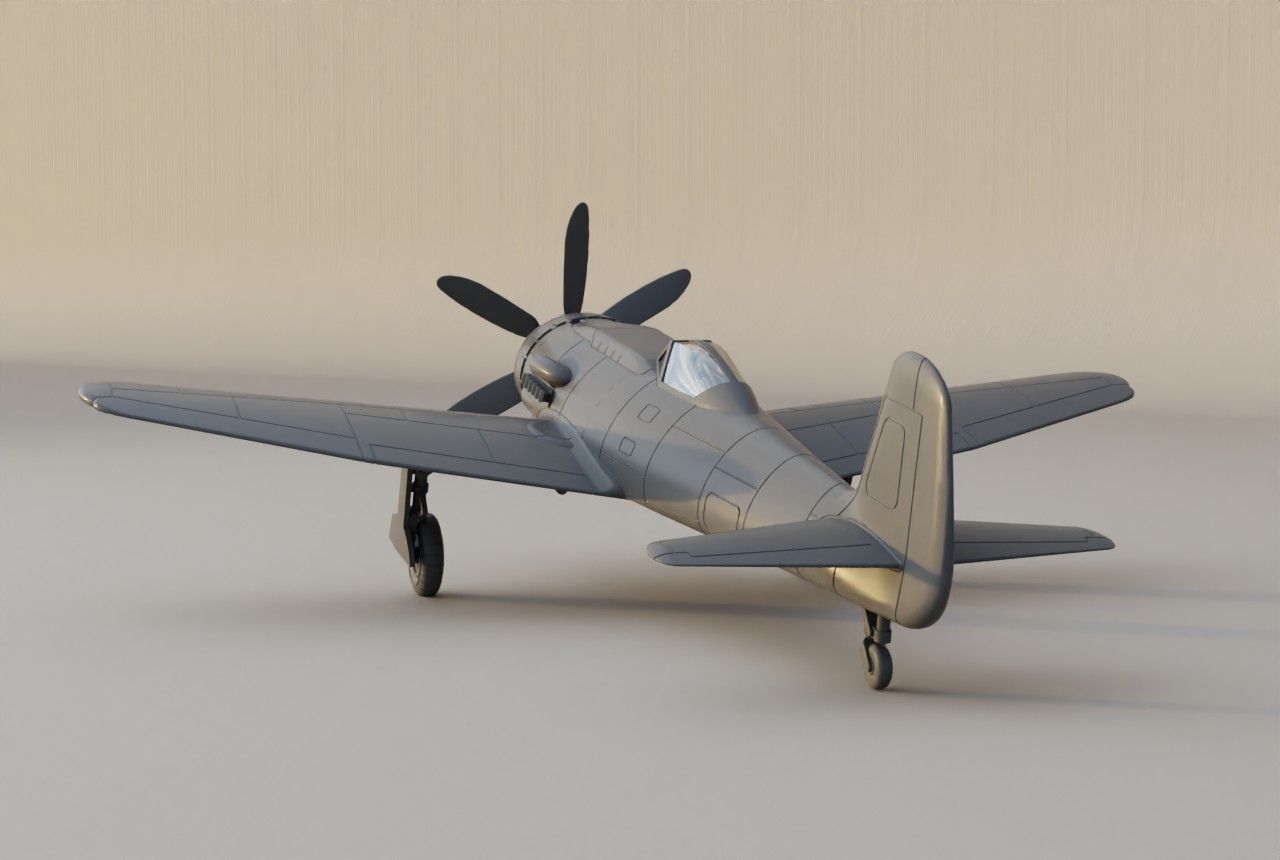
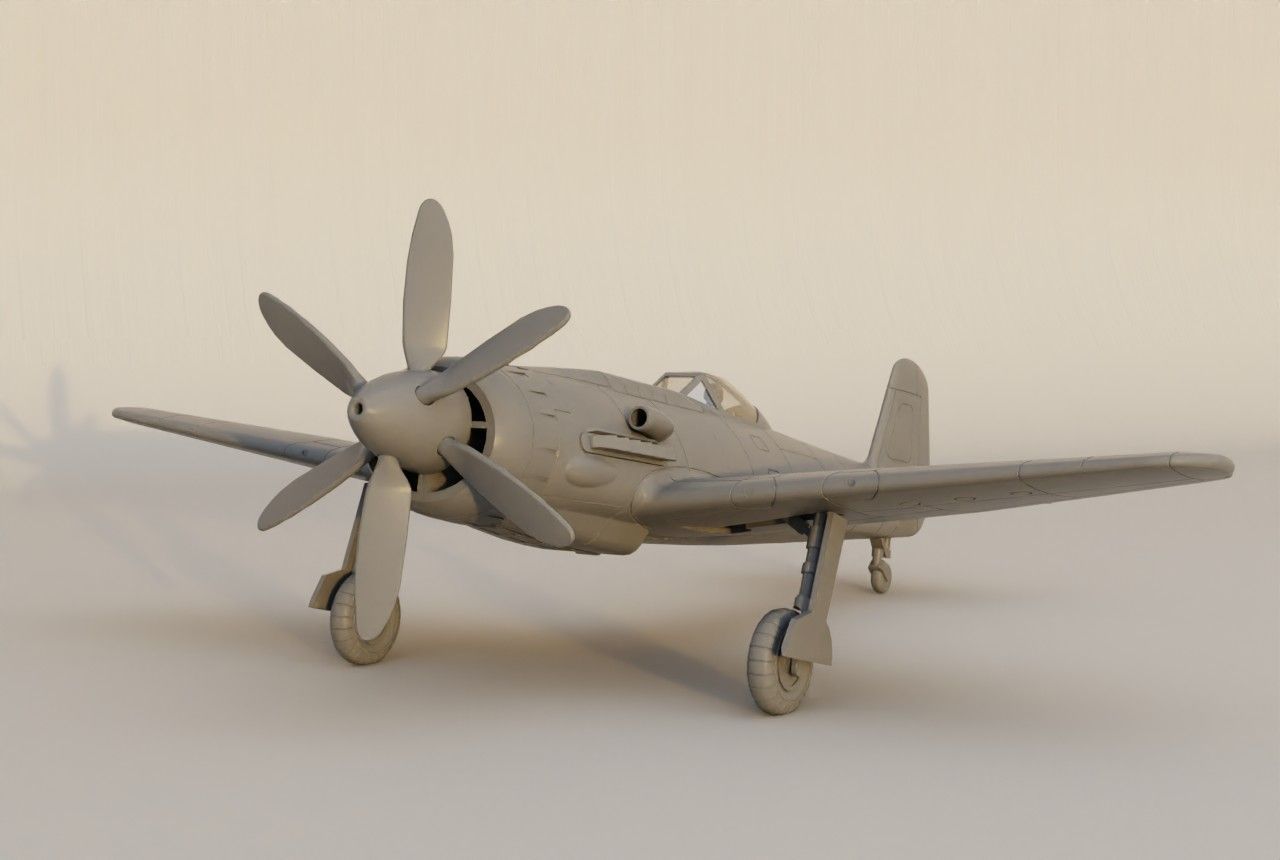
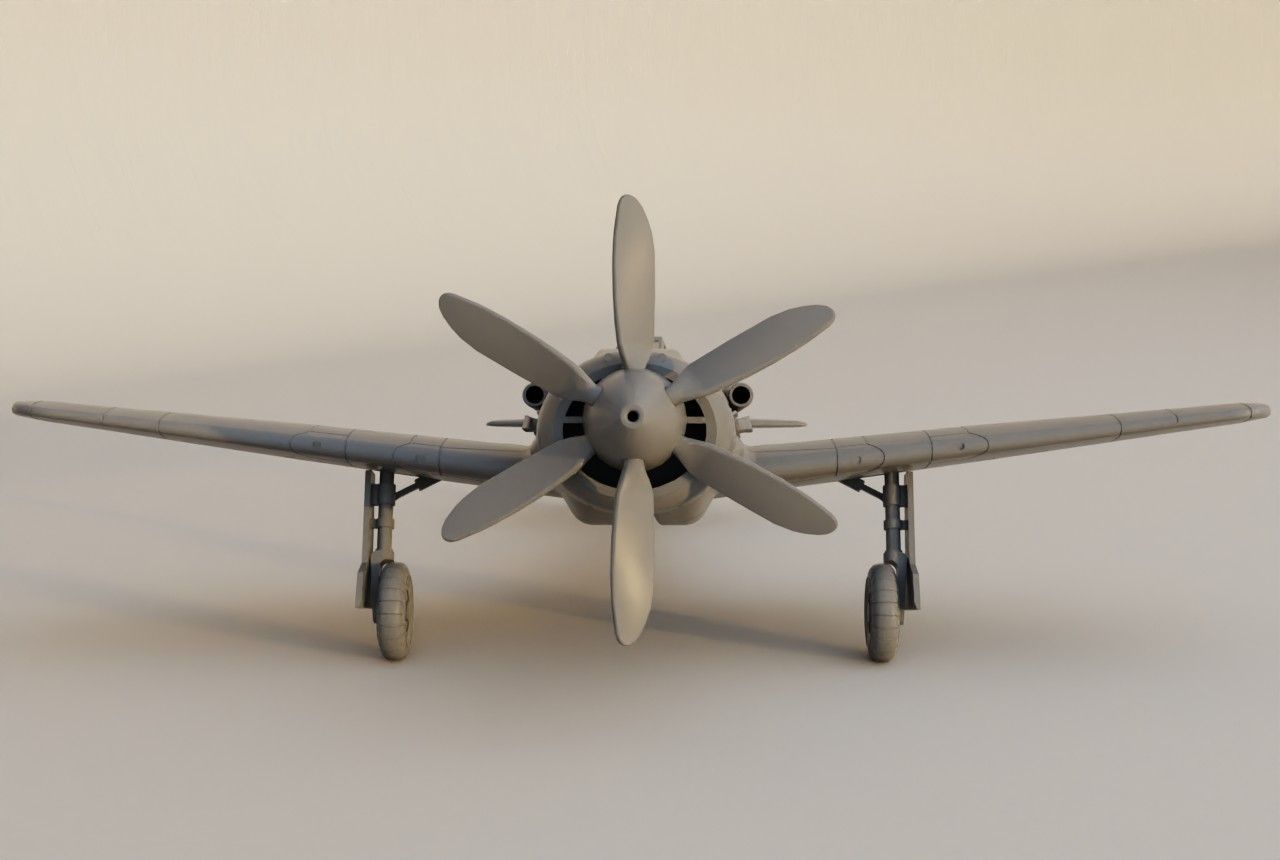
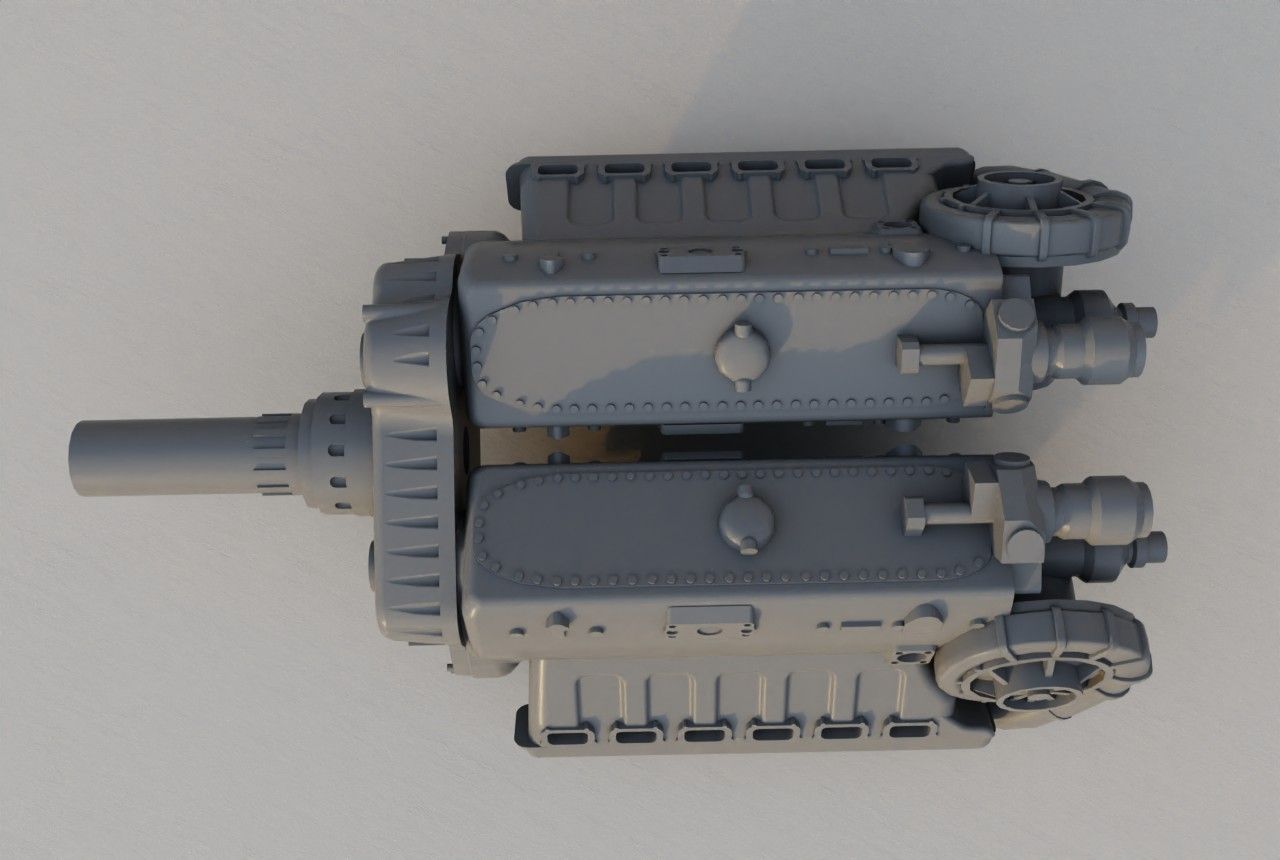
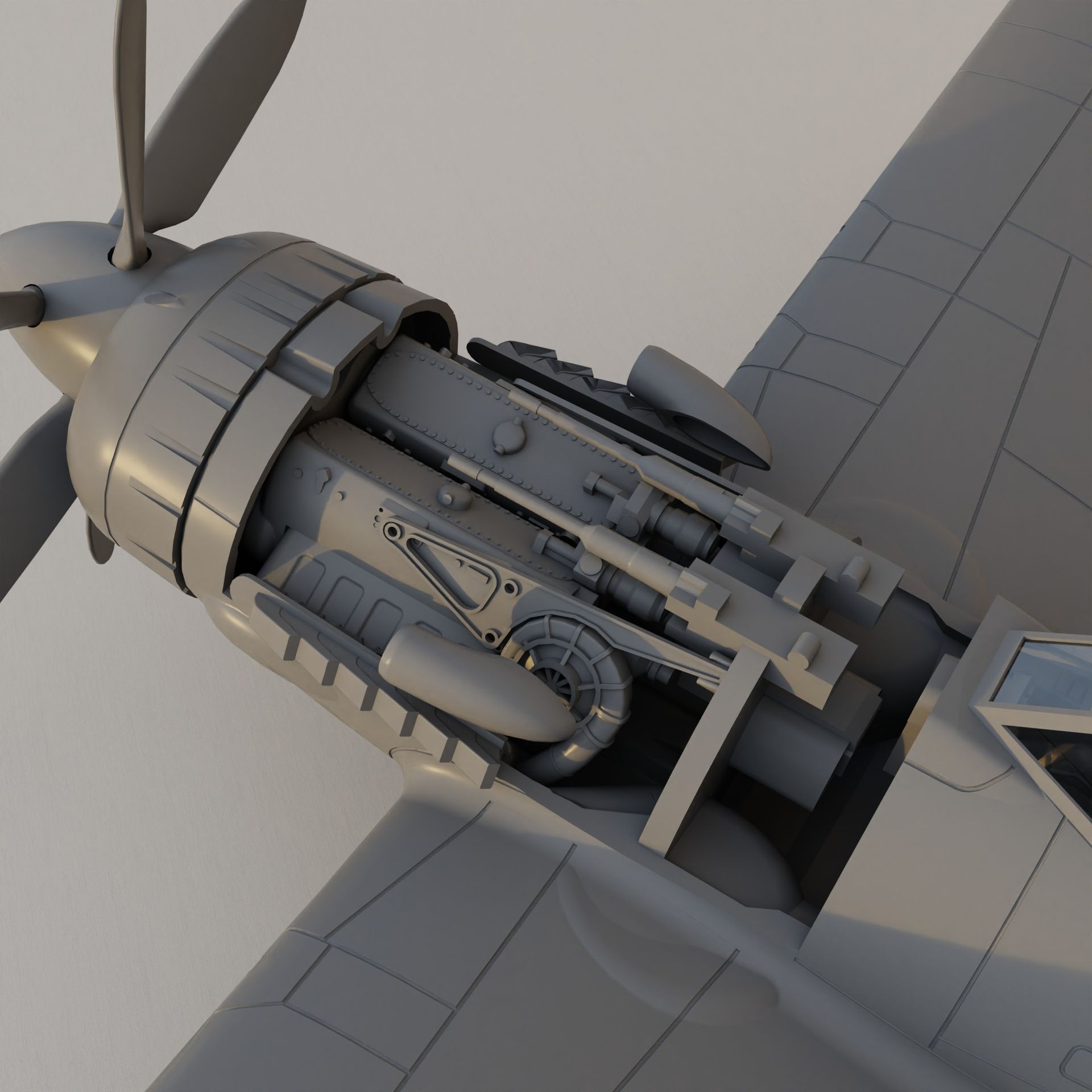
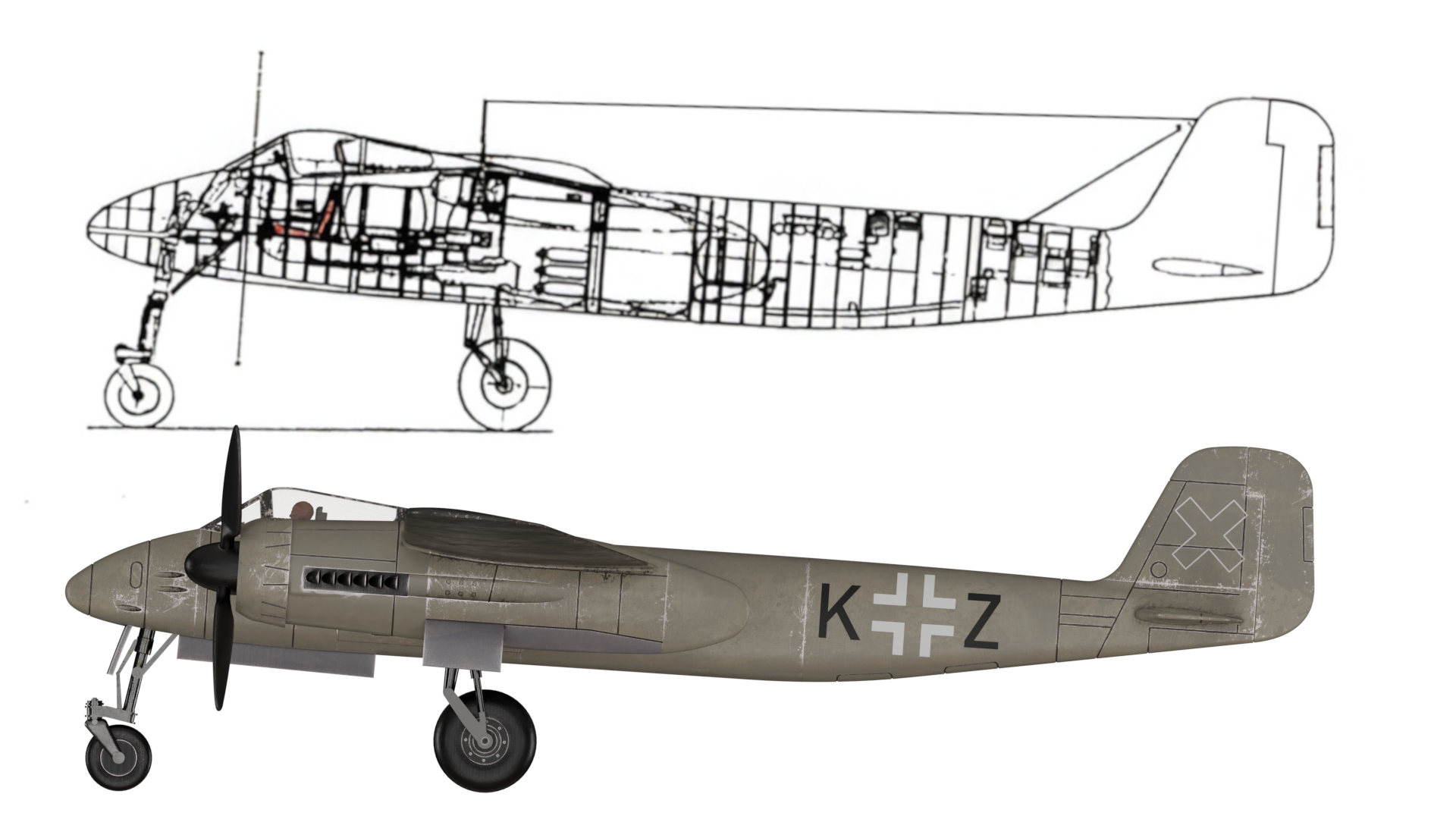
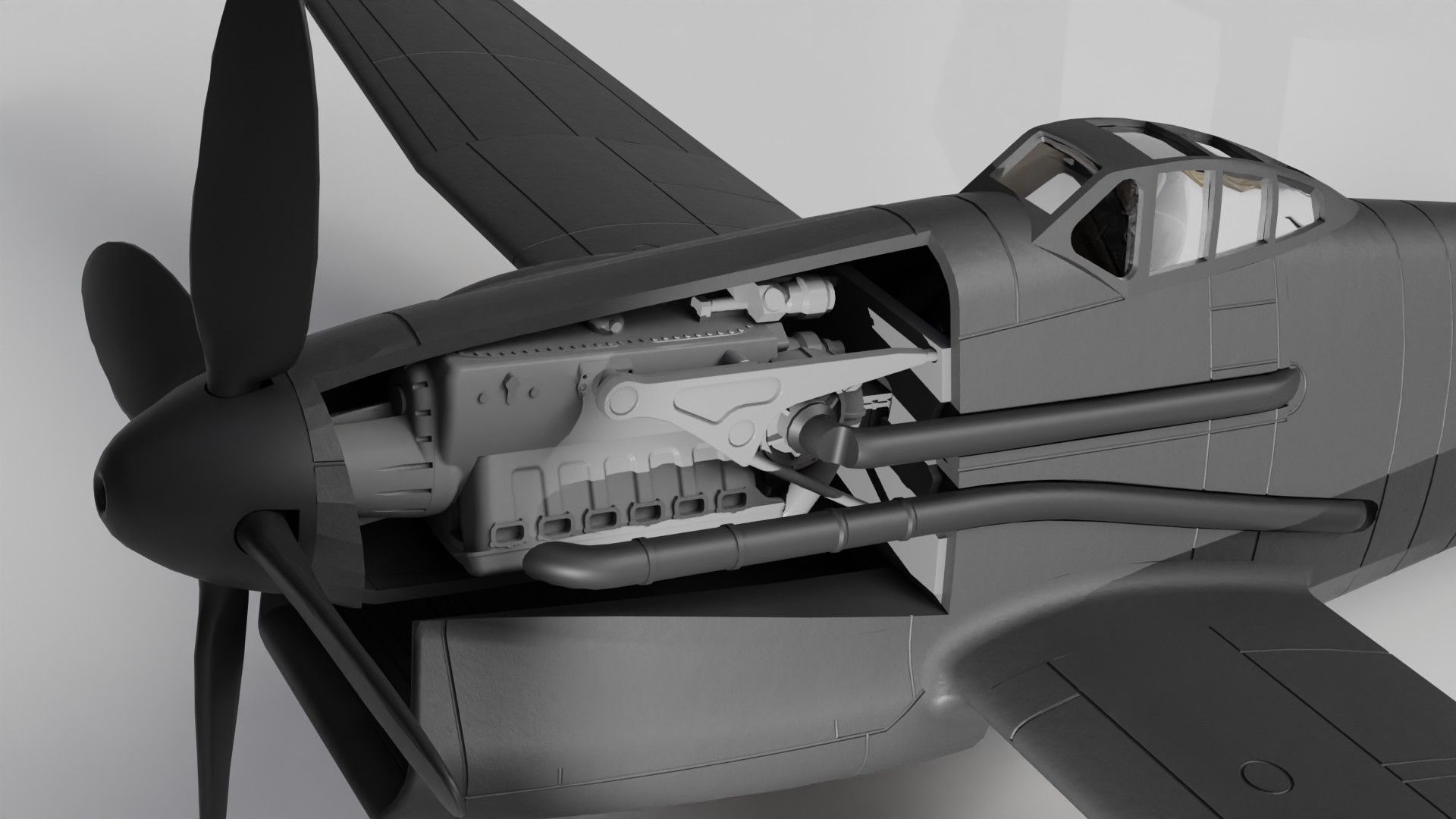
The EF 110 was proposed by Junkers as a ‘Schnellstbomber’ (engl. fast bomber). The EF 110 featured a single fuselage design housing a powerful DB 613 engine, essentially twin DB 603s merged, propelling contra-rotating props at its nose. This configuration resulted in an exceptionally broad fuselage, accommodating two 500 kg bombs side by side within its internal bomb bay. The sole schematic of the aircraft, is dated December 11, 1942.
Junkers EF 110
Design of the EF 110
The powerplant: DB 613
Engine Cooling
Armament
The Kit
The kit is available here: SHOP

Bringing the Heinkel P.1068 to Life For aviation history enthusiasts and model builders, the Heinkel P.1068 is one of the lesser-known yet highly intriguing Luft ’46 aircraft concepts. Originally developed as a twin-engine competitor to the Arado Ar 234 , it evolved into a more advanced bomber featuring up to six engines. Though the He 343 project was ultimately canceled, the P.1068 survived in a different form—as a test aircraft built in collaboration with DFS (Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug) . Now, you can bring this advanced jet bomber concept to life with our latest Heinkel P.1068-01 model kit , available exclusively at My3DBase .
Damit Eure Kekse mit unseren Backförmchen so richtig gut funktionieren haben wir für euch ein paar Tips zusammengestellt. Vorab einmal das Rezept: 100 g Butter 50 g Puderzucker (kann dem eigenen Geschmack angepasst werden) 30 g Ei 200 g Mehl Die Mengen können unter Einhaltung des Mischungsverhältnisses erhöht werden. Zunächst wird der Puderzucker mit der Butter vermengt. Danach wir das Ei hinzugegeben. Anschließend wird das Mehl untergehoben. Wichtig: Damit der Teig die richtige Konsistenz erhält sollte er gekühlt werden; ca 30min im Gefrierfach oder 1-2 Stunden im Kühlschrank.